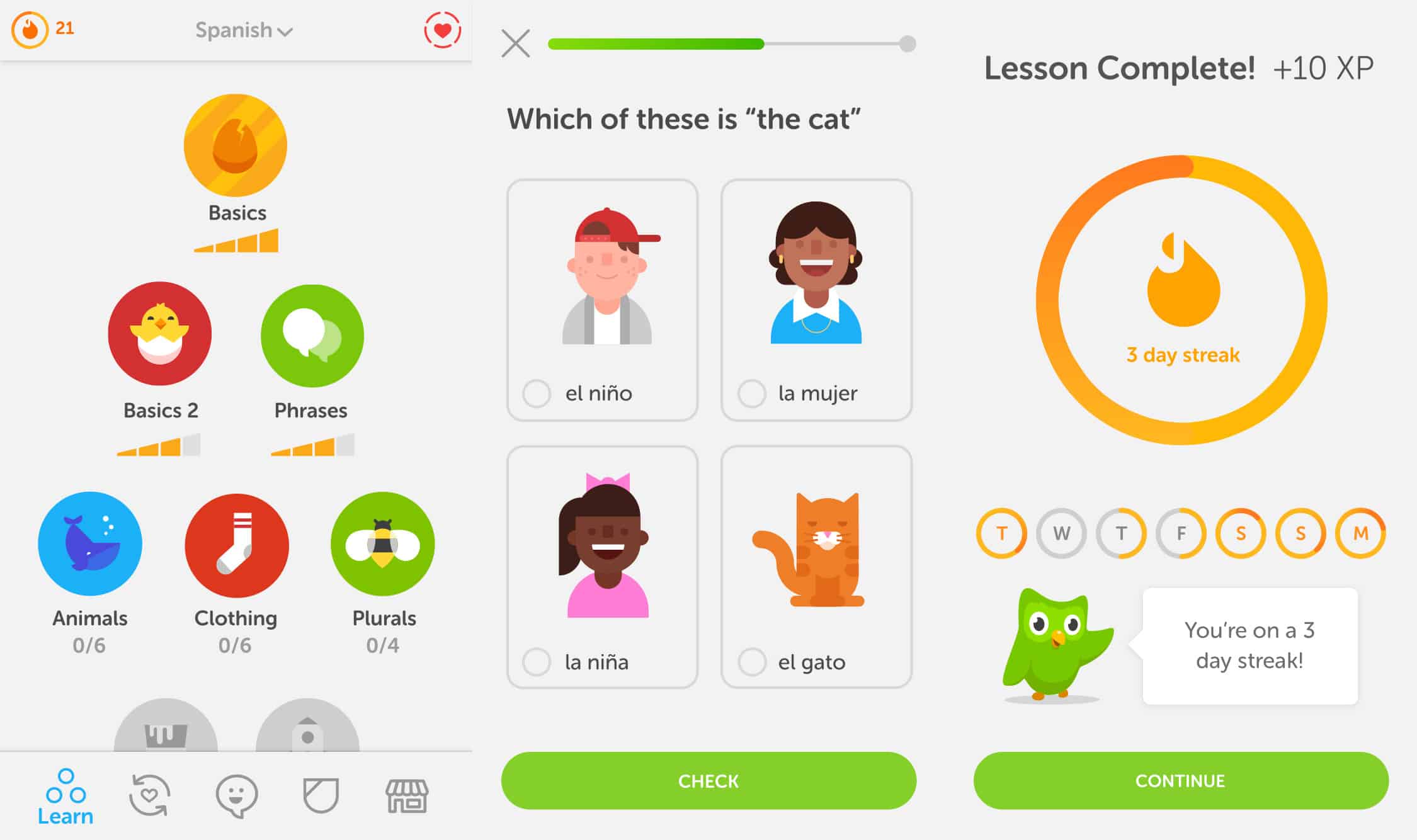
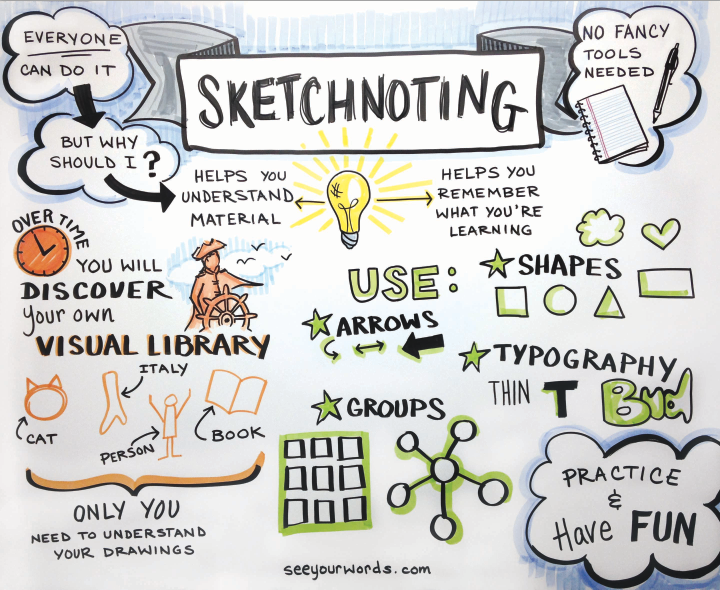
After this week of study, I realized that sketchnoting is a very effective way of studying new knowledge and remember them. What is sketchnoting? It is a method of taking notes and organize knowledge. While you draw pictures to illustrate your words in your notes, you have to understand first, then draw it based on your understanding. That’s how sketchnoting help you understand the knowledge. Furthermore, using arrows and icons to organize the notes makes your brain clearer about those notes. Instead of full of words in the page, the combination of words and images makes notes more interesting and easier to read. For me, I’m not good at drawing, but simple images work well in the notes. I use arrows and lists the most to organize my notes. These are easy and save time during lectures.
According to Mayer’s theory, the Signaling Principle, the Contiguity Principle, the Redundancy Principle, the Coherence Principle, the Segmenting Principle, Mayer’s Pretraining Principle and the Modality Principle are all included in sketchnoting. While the Redundancy Principle, the Coherence Principle and Mayer’s Pretraining Principle are used to process texts that simplify tangential information into important points, the other four principles act on visuals. As the Modality Principle states, graphics use the working memory capacity more effectively to help the learner to “hold” the content and remember it for a longer time. The Signaling Principle, the Contiguity Principle and the Segmenting Principal work more on organizing notes to make notes more clear and easier to read.
Reference
The Modality Principle – How and when to use it.
Youtube video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y_fn2fpO5cU